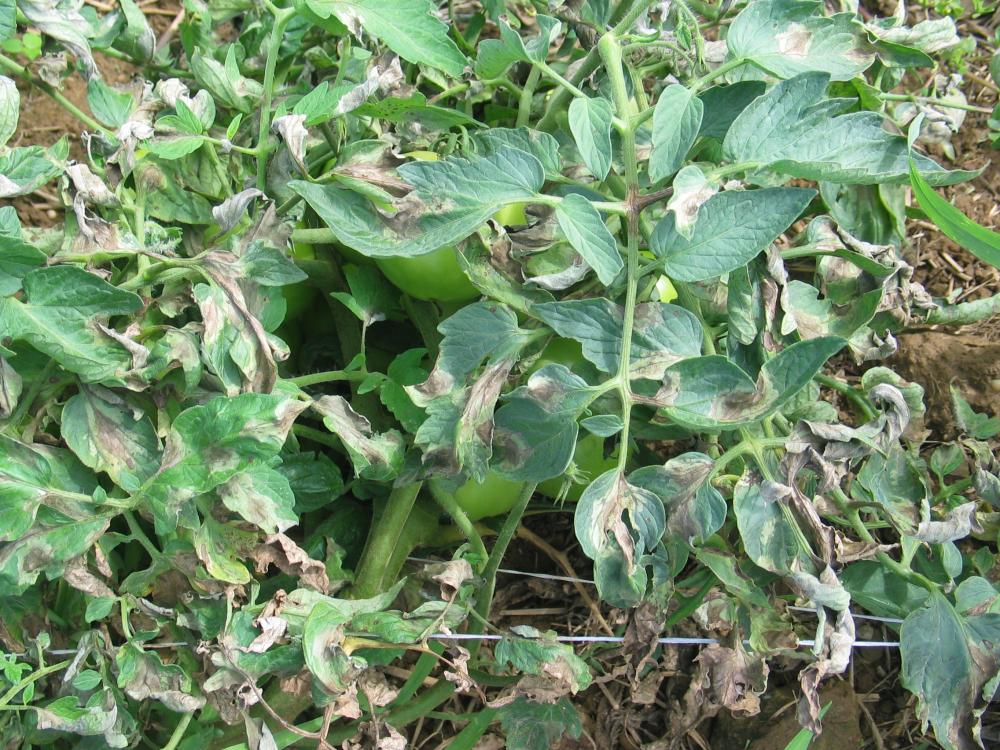
Late blight Management for Fall Rutgers University Potato late blight is arguably one of the most infamous diseases in agriculture. Historically, it is best known as the cause of the Irish potato famine of the 1840s, which resulted in the death or emigration of over 2 million people from Ireland (Martin et al. 2013).
Late Blight Management in Tomato with Resistant Varieties
Potato Late Blight Plant Diseases Chapter 1 Epidemic. Late blight is caused by the fungus-like comycete pathogen Phytophthora infestans. This potentially devastating disease can infect potato foliage and tubers at any stage of crop development. This potentially devastating disease can infect potato foliage and tubers at any stage of crop development., Lewis W. Jett, Horticulture Specialist, May 2010 Available in PDF format What is late blight? Late blight (Phytophthora infestans) is one of the most serious fungal diseases that ….
Once Late Blight sinks its teeth into your tomato or potato patch, fungicide will have minimal control over it, but Early Blight may be controlled with proper fungicide use. See this excellent fact sheet from Purdue University on the different fungicides available for organic gardeners . Tomato stems and leaves. Tomato plants are also susceptible to late blight, and the foliar symptoms are similar to those on potato. Like potato, infected tomato plants (Figure 11) may be rapidly infected and destroyed by P. infestans.
Download the PDF version. An Article Written by Nancy DuBrule-Clemente. Last summer, factors converged to create the perfect situation for an infestation of late blight, a devastating disease of tomatoes and potatoes. In interior districts where late blight occurs sporadically, watch for disease symptoms during routine field monitoring, and record your results (example form— 108 KB, PDF). Apply fungicides when late blight lesions appear in the field or in nearby plantings.
Efficacy of some fungicides against late blight of tomato. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci., 17: 465-469 The influence of some fungicides, recommended for use in Bulgaria for control of late blight of tomato, was 3 UH–CTAHR Late Blight of Tomato (Photyphthora infestans) PD-45 — Aug. 2008 Table 1. Reported plant hosts worldwide of the plant pathogen Phytophthora infestans (after Erwin and Ri-
Life cycle of Phytophthora infestans, causal agent of late blight of potato and tomato. The blight fungus parasitizes potato plants and closely related plants in South America. Farmers there grow an enormous number of potato cultivars that vary in their susceptibility to the parasite, so that even though some loss to the parasite occurs, devastating epidemics are avoided. The technology of Phytophthora infestans symptoms (late blight) on potato stem in the field. Thorsten Kraska, University of Bonn, Germany Tuber blight on potato
Controlling highly destructive plant diseases such as potato and tomato late blight, caused by the oomycete Phytophthora infestans, with non-fungicidal alternative products is a difficult but necessary task that needs to be accomplished. Late blight is caused by the fungus-like comycete pathogen Phytophthora infestans. This potentially devastating disease can infect potato foliage and tubers at any stage of crop development. This potentially devastating disease can infect potato foliage and tubers at any stage of crop development.
Late blight of tomato and potato is a potentially destructive fungal disease in Maryland home gardens. This is the same disease that caused the Irish potato famine in the 1840s. Late blight can occur at any time during the growing season when the weather is cool and wet. The disease is slowed down by a return to hot, dry weather. Gardeners in cooler areas of Maryland may see late blight Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(7): 779-784 Efficacy of Certain Bio-Agents and Plant Extracts against Late Blight (Phytophthora infestans) of Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum
Late blight will not survive on tomato stakes and cages. In some parts of the world, late blight has two ‘mating types’ (the fungal equivalent of male and female) which can produce long-lasting ‘oospores’ that survive independently. The most sustainable strategy to manage tomato late blight (LB) would be to deploy an integrated system including cultural practices, fungicide application, and the use of cultivars with broad
D. R. Panthee et al. 2146 (a) (b) (c) (d) Figure 1. Molecular markers associated with Ph-3 mediated late blight resistance in tomato. In the gel, the sample order is: 1: In interior districts where late blight occurs sporadically, watch for disease symptoms during routine field monitoring, and record your results (example form— 108 KB, PDF). Apply fungicides when late blight lesions appear in the field or in nearby plantings.
Lewis W. Jett, Horticulture Specialist, May 2010 Available in PDF format What is late blight? Late blight (Phytophthora infestans) is one of the most serious fungal diseases that … Late Blight (Phytophthora infestans) •Responsible for entire crop losses in the Solanaceae family such as tomato, potato, and eggplant in less than 5 days
The most sustainable strategy to manage tomato late blight (LB) would be to deploy an integrated system including cultural practices, fungicide application, and the use of cultivars with broad‐spectrum genetic resistance against LB. Late blight affects foliage of both potato and tomato as well as potato tubers and tomato fruit. Late blight is a very difficult disease to manage organically. Organic farmers should employ all strategies available to reduce late blight risk in host crops.
Potato late blight British Society for Plant Pathology
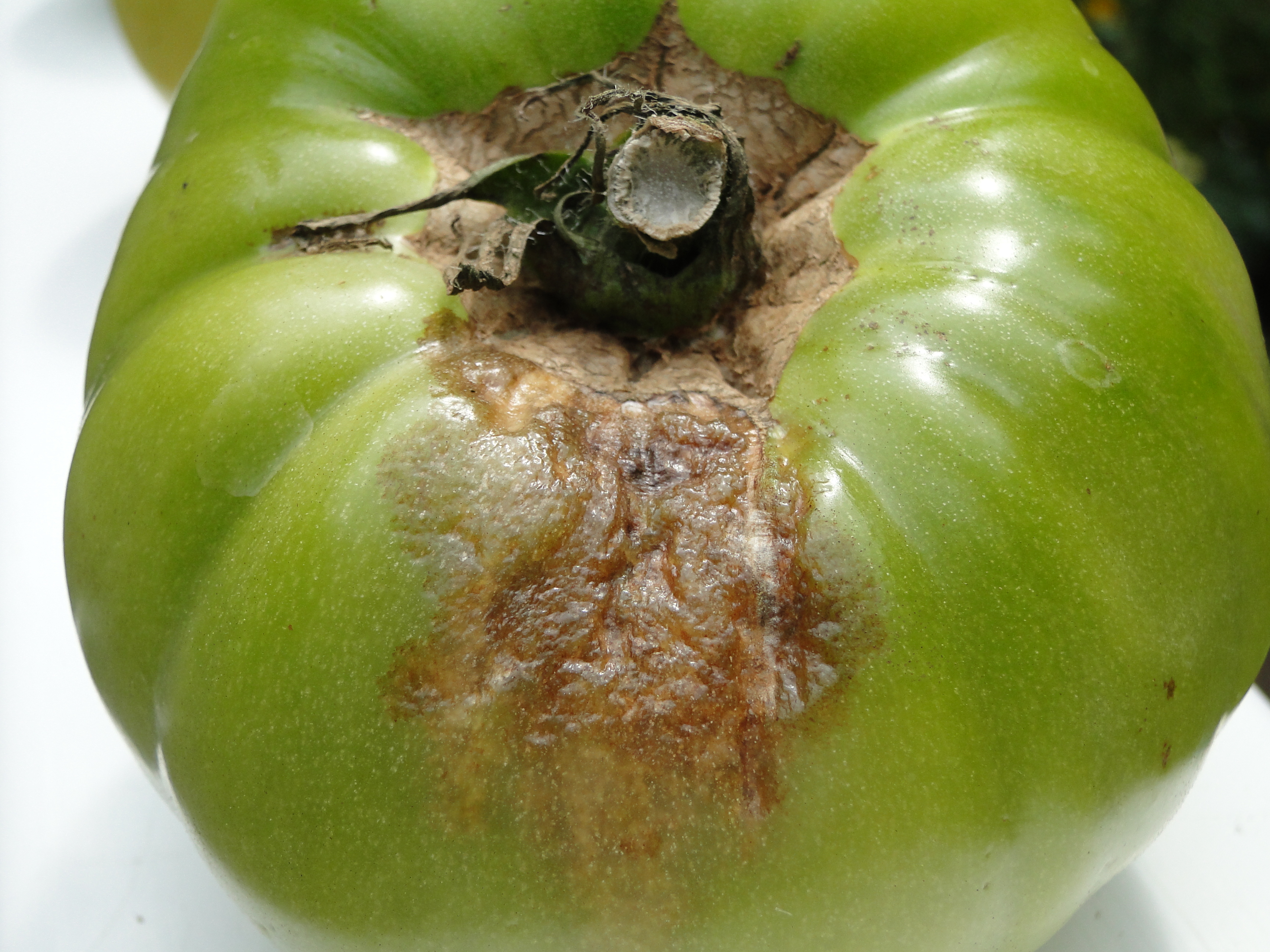

EFFICACY OF SOME FUNGICIDES AGAINST LATE BLIGHT OF TOMATO. Potato late blight is arguably one of the most infamous diseases in agriculture. Historically, it is best known as the cause of the Irish potato famine of the 1840s, which resulted in the death or emigration of over 2 million people from Ireland (Martin et al. 2013)., The most sustainable strategy to manage tomato late blight (LB) would be to deploy an integrated system including cultural practices, fungicide application, and the use of cultivars with broad‐spectrum genetic resistance against LB..
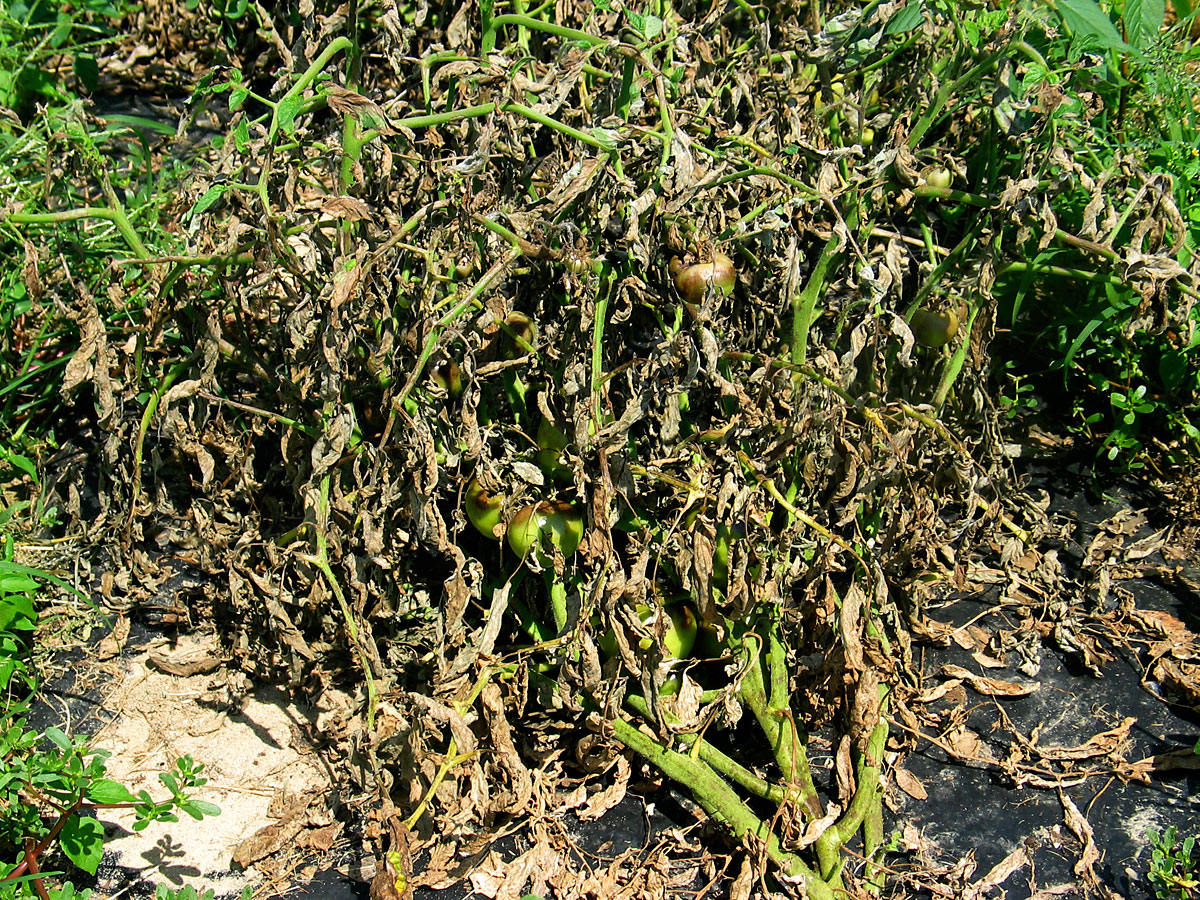

Tomato Cultivar Specifics and Ref. of LB/EB Genetic. 1 INTRODUCTION Late blight is a potentially serious fungal disease of potato and tomato. The fungus-like microrganism, Phytophthora infestans, was responsible for the infamous Irish potato, 1 Publication ANR-6 Introduction Late blight, caused by Phytophthora infestans, is an important and destructive disease on potato and tomato. It.
Potato Late Blight Plant Diseases Chapter 1 Epidemic
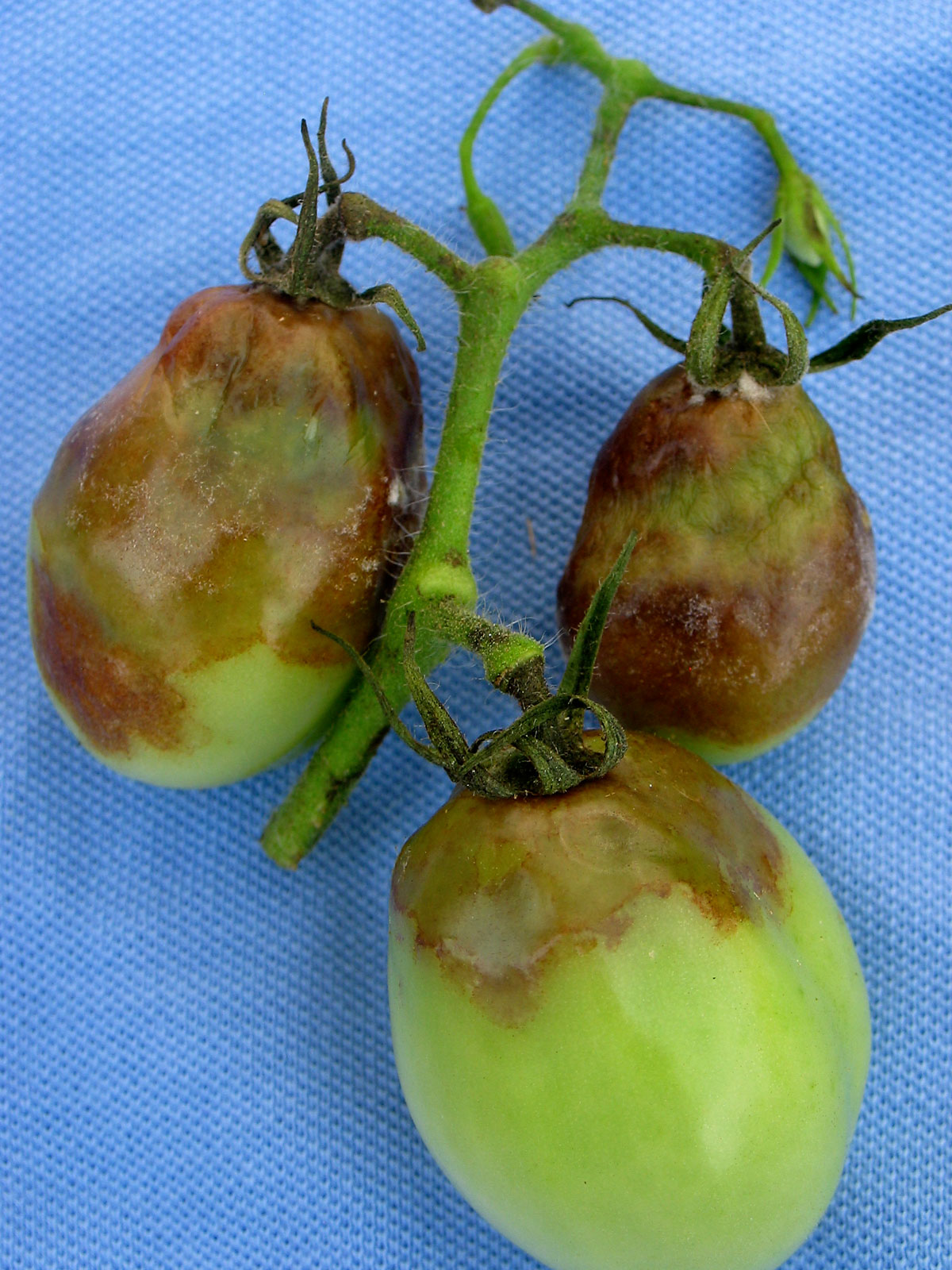

Late Blight on Tomato and Potatoes UMass Amherst. Late blight is a destructive disease of tomatoes and potatoes that can kill plants, and make tomato fruits and potato tubers inedible. This disease also affects, although typically to a lesser extent, weeds such as nightshade. Historically, late blight was responsible, in part, for the Irish potato famine, which led to the death of at least one million Irish, and the emigration of another one 1 Publication ANR-6 Introduction Late blight, caused by Phytophthora infestans, is an important and destructive disease on potato and tomato. It.

Once late blight is present, only foliar fungicide applications can manage late blight in the field. (A current list of fungicides can be found in the NDSU “Fungicide Guide,” PP622). (A current list of fungicides can be found in the NDSU “Fungicide Guide,” PP622). 1 INTRODUCTION Late blight is a potentially serious fungal disease of potato and tomato. The fungus-like microrganism, Phytophthora infestans, was responsible for the infamous Irish potato
Late blight of potatoes and tomatoes, the disease that was responsible for the Irish potato famine in the mid-nineteenth century, is caused by the fungus-like oomycete pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Late Blight (Phytophthora infestans) •Responsible for entire crop losses in the Solanaceae family such as tomato, potato, and eggplant in less than 5 days
Late blight is a destructive disease of tomatoes and potatoes that can kill plants, and make tomato fruits and potato tubers inedible. This disease also affects, although typically to a lesser extent, weeds such as nightshade. Historically, late blight was responsible, in part, for the Irish potato famine, which led to the death of at least one million Irish, and the emigration of another one 108 DISEASE MANAGEMENT: Late Blight References: Figure 4. Tomato seedling stunted. Photograph by: Pam Roberts. Dr. Pamela D. Roberts UF/IFAS SWFREC
Importance Late blight is an extremely important and damaging disease of tomatoes and potatoes, and can be found nearly anywhere these crops are produced. Potato late blight is arguably one of the most infamous diseases in agriculture. Historically, it is best known as the cause of the Irish potato famine of the 1840s, which resulted in the death or emigration of over 2 million people from Ireland (Martin et al. 2013).
In interior districts where late blight occurs sporadically, watch for disease symptoms during routine field monitoring, and record your results (example form— 108 KB, PDF). Apply fungicides when late blight lesions appear in the field or in nearby plantings. HOW WE MANAGE TOMATO LATE BLIGHT ON OUR FARM Anthony Emmi Emmi & Sons Inc. 1482 West Genesee Road Baldwinsville, New York 13027 Late Blight disease develops in high moisture conditions and moderate temperatures.
Late Blight: Phytophthora infestans New York gardeners are sometimes surprised by a quick and apparently spontaneous blighting and death of their potato and tomato plants during wet PLPA-Pot009-02 Prepared by Dr. Diana Schultz1 and Dr. Ronald D. French2 1Plant Pathologist (Fort Myers, Florida) 2Assistant Professor and Extension Plant Pathologist (Amarillo, TX)
HOW WE MANAGE TOMATO LATE BLIGHT ON OUR FARM Anthony Emmi Emmi & Sons Inc. 1482 West Genesee Road Baldwinsville, New York 13027 Late Blight disease develops in high moisture conditions and moderate temperatures. tomato and potato late blight alert what every grower needs to know about tomato and potato late blight 13109 schavey rd., suite 7 dewitt, mi 48820
Importance Late blight is an extremely important and damaging disease of tomatoes and potatoes, and can be found nearly anywhere these crops are produced. Life cycle of Phytophthora infestans, causal agent of late blight of potato and tomato. The blight fungus parasitizes potato plants and closely related plants in South America. Farmers there grow an enormous number of potato cultivars that vary in their susceptibility to the parasite, so that even though some loss to the parasite occurs, devastating epidemics are avoided. The technology of
108 DISEASE MANAGEMENT: Late Blight References: Figure 4. Tomato seedling stunted. Photograph by: Pam Roberts. Dr. Pamela D. Roberts UF/IFAS SWFREC PLPA-Pot009-02 Prepared by Dr. Diana Schultz1 and Dr. Ronald D. French2 1Plant Pathologist (Fort Myers, Florida) 2Assistant Professor and Extension Plant Pathologist (Amarillo, TX)
1 INTRODUCTION Late blight is a potentially serious fungal disease of potato and tomato. The fungus-like microrganism, Phytophthora infestans, was responsible for the infamous Irish potato Potato late blight is arguably one of the most infamous diseases in agriculture. Historically, it is best known as the cause of the Irish potato famine of the 1840s, which resulted in the death or emigration of over 2 million people from Ireland (Martin et al. 2013).
moved into WI from other nearby states with reports of late blight on tomato and potato. The late blight pathogen produces a lot of spores on infected plants and spores can move in air up to Late blight will not survive on tomato stakes and cages. In some parts of the world, late blight has two ‘mating types’ (the fungal equivalent of male and female) which can produce long-lasting ‘oospores’ that survive independently.
Late Blight on Potato and Tomato University of Florida
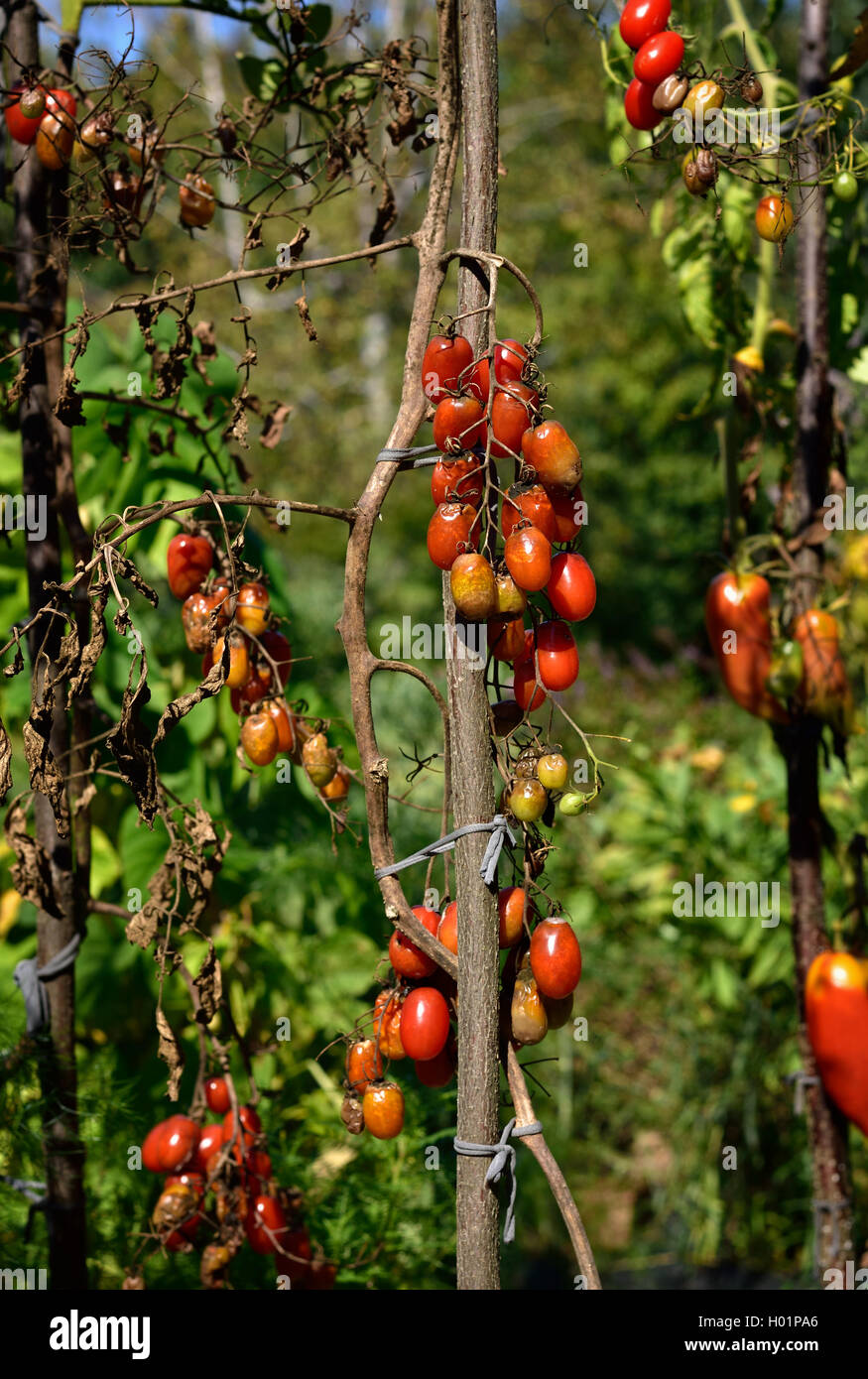

Managing Late Blight in Tomato and Potato – An Essential. A national cooperative effort (funded by USDA-NIFA) on Late Blight of Tomato and Potato in the U.S. This site serves as an information portal on late blight. You can report disease occurrences, submit a sample online, observe disease occurrence maps, and sign up for text disease alerts., This fact sheet explains the basics about late blight tomato disease and practical ways . to control it. Late blight (Phytophthora infestans) is one of the most serious fungal diseases that can affect tomatoes and potatoes. Late blight is spread from infected transplants, volunteer potato or tomato plants, How is it and certain weeds botanically related to tomatoes. Spores of this fungus can.
Plant Pathology Fact Sheet Late Blight of Tomato
Late Blight of Potato and Tomato (Mar 2016) (PDF 292 KB). This fact sheet explains the basics about late blight tomato disease and practical ways . to control it. Late blight (Phytophthora infestans) is one of the most serious fungal diseases that can affect tomatoes and potatoes. Late blight is spread from infected transplants, volunteer potato or tomato plants, How is it and certain weeds botanically related to tomatoes. Spores of this fungus can, Table 1. Tomato cultivars tested for late blight resistance against the US-22, US-23, and US-24 clonal lineages of Phytophthora infestans and their resistance/susceptibility response..
Late Blight A Serious Disease of. Potatoes and Tomatoes Late Blight Symptoms. On potato tubers: Infected potatoes have shallow, brownish or purplish lesions on the surface of the tuber. D. R. Panthee et al. 2146 (a) (b) (c) (d) Figure 1. Molecular markers associated with Ph-3 mediated late blight resistance in tomato. In the gel, the sample order is: 1:
When choosing a pesticide, consider its usefulness in an IPM program by reviewing the pesticide's properties, efficacy, application timing, and information relating to resistance management, honey bees (PDF), and environmental impact. "I lost all my tomato crop to late blight this year - except Matt's Wild Cherry and it is a great tasting sweet little tomato. Phil Evans on Monday 28 September 2015 "I've been growing Matt's Wild Cherry for 20 years and agree that it is blight tolerant and great tasting.
The causal pathogen of late blight from potatoes was first described in 1845 by Montagne and from tomato in 1847 by Payen in France. However, it was 1863 before deBary established beyond doubt that this organism, Phytophthora infestans, was the cause of late blight. The disease occurs worldwide Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(7): 779-784 Efficacy of Certain Bio-Agents and Plant Extracts against Late Blight (Phytophthora infestans) of Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum
2009 Tomato Disease Resistance Breeding Annual Report to PVMRP 1 Development of Early Blight and Late Blight Resistant Tomatoes Report of a research supported by: Late Blight (Phytophthora infestans) •Responsible for entire crop losses in the Solanaceae family such as tomato, potato, and eggplant in less than 5 days
Controlling highly destructive plant diseases such as potato and tomato late blight, caused by the oomycete Phytophthora infestans, with non-fungicidal alternative products is a difficult but necessary task that needs to be accomplished. Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(7): 779-784 Efficacy of Certain Bio-Agents and Plant Extracts against Late Blight (Phytophthora infestans) of Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum
Late blight will not survive on tomato stakes and cages. In some parts of the world, late blight has two ‘mating types’ (the fungal equivalent of male and female) which can produce long-lasting ‘oospores’ that survive independently. Managing Late Blight in Tomato and Potato – An Essential Part of Gardening Meg McGrath, Department of Plant Pathology and Plant-Microbe Biology, Cornell University
Late blight, caused by the pathogen Phytophthora infestans , was a disease once considered sporadic, but is now an annual concern for tomato and potato growers in Late blight is a destructive disease of tomatoes and potatoes that can kill plants, and make tomato fruits and potato tubers inedible. This disease also affects, although typically to a lesser extent, weeds such as nightshade. Historically, late blight was responsible, in part, for the Irish potato famine, which led to the death of at least one million Irish, and the emigration of another one
Potato late blight is arguably one of the most infamous diseases in agriculture. Historically, it is best known as the cause of the Irish potato famine of the 1840s, which resulted in the death or emigration of over 2 million people from Ireland (Martin et al. 2013). Tomato stems and leaves. Tomato plants are also susceptible to late blight, and the foliar symptoms are similar to those on potato. Like potato, infected tomato plants (Figure 11) may be rapidly infected and destroyed by P. infestans.
The causal pathogen of late blight from potatoes was first described in 1845 by Montagne and from tomato in 1847 by Payen in France. However, it was 1863 before deBary established beyond doubt that this organism, Phytophthora infestans, was the cause of late blight. The disease occurs worldwide Late blight is a destructive disease of tomatoes and potatoes that can kill plants, and make tomato fruits and potato tubers inedible. This disease also affects, although typically to a lesser extent, weeds such as nightshade. Historically, late blight was responsible, in part, for the Irish potato famine, which led to the death of at least one million Irish, and the emigration of another one
The most sustainable strategy to manage tomato late blight (LB) would be to deploy an integrated system including cultural practices, fungicide application, and the use of cultivars with broad Phytophthora infestans is an oomycete or water mold, a microorganism that causes the serious potato and tomato disease known as late blight or potato blight.
Late Blight in Potato PP1849 - NDSU Agriculture and
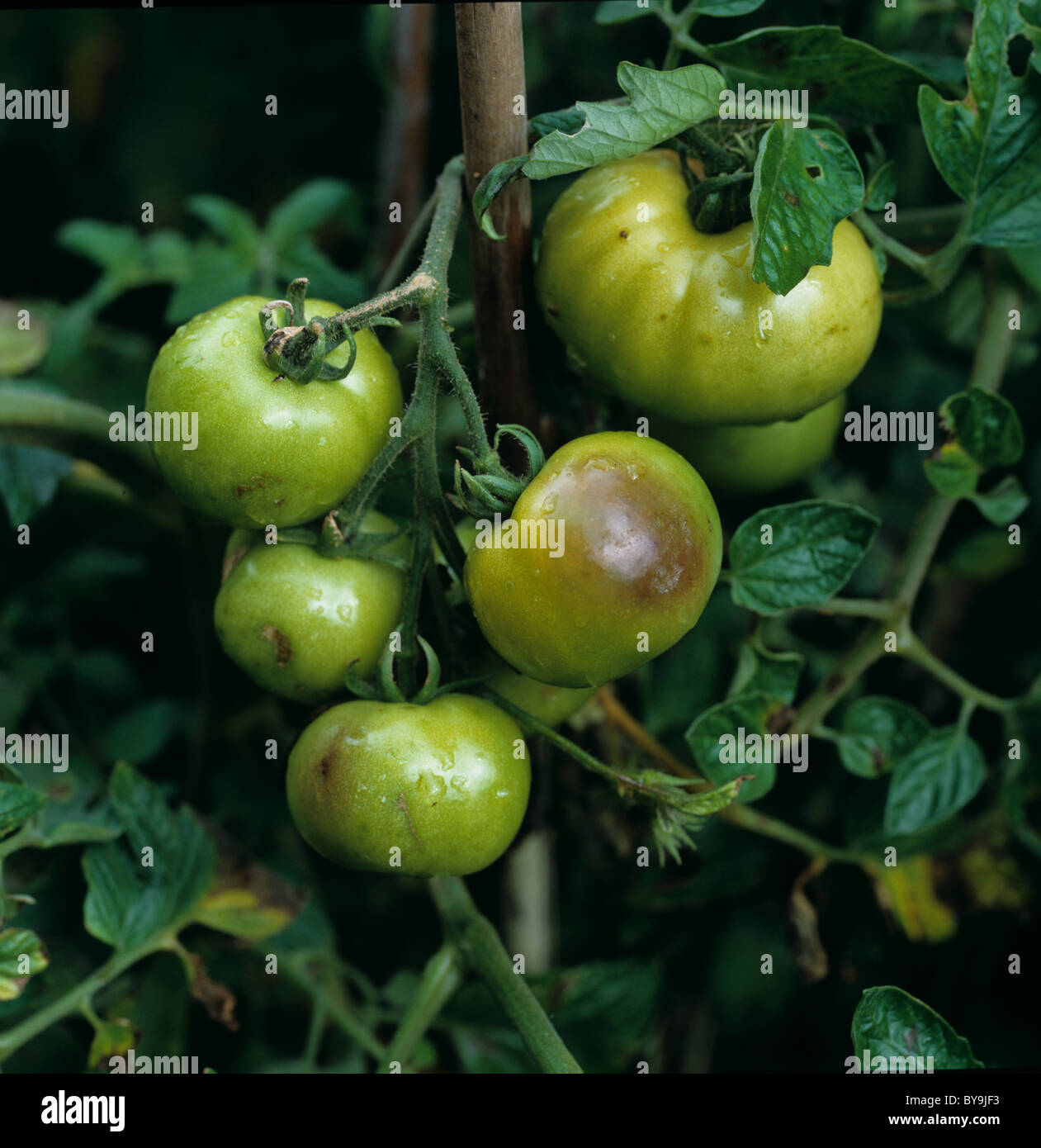

Late Blight Management in Tomato with Resistant Varieties. Late blight of tomato and potato is a potentially destructive fungal disease in Maryland home gardens. This is the same disease that caused the Irish potato famine in the 1840s. Late blight can occur at any time during the growing season when the weather is cool and wet. The disease is slowed down by a return to hot, dry weather. Gardeners in cooler areas of Maryland may see late blight, Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(7): 779-784 Efficacy of Certain Bio-Agents and Plant Extracts against Late Blight (Phytophthora infestans) of Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum.
TOMATO AND POTATO LATE BLIGHT ALERT MSU Extension
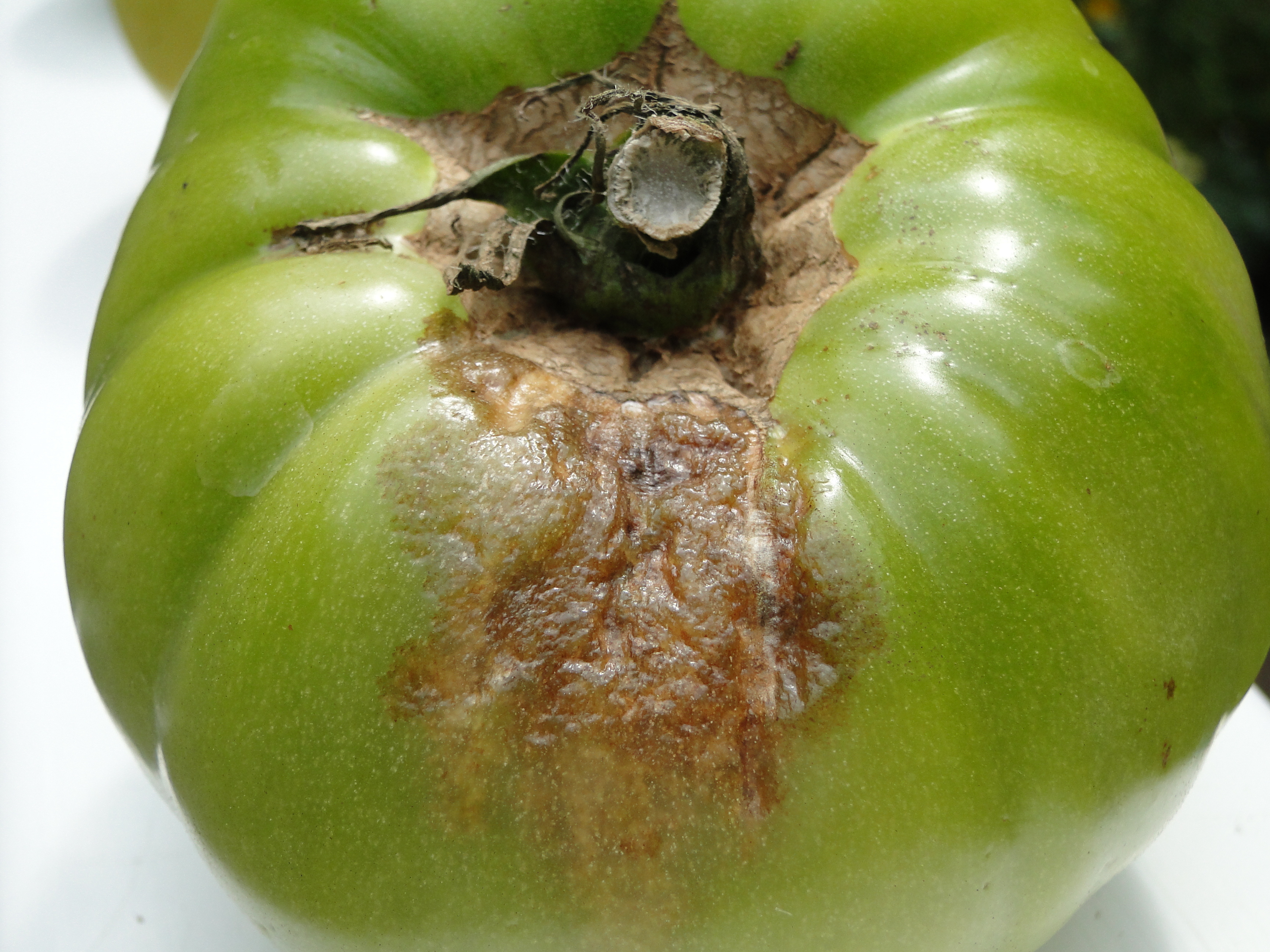

Understanding Late Blight of Tomatoes Extension Service. PLPA-Pot009-02 Prepared by Dr. Diana Schultz1 and Dr. Ronald D. French2 1Plant Pathologist (Fort Myers, Florida) 2Assistant Professor and Extension Plant Pathologist (Amarillo, TX) Late blight tomato disease is the rarest of the blights that affect both tomatoes and potatoes, but it is also the most destructive. It was the leading factor in the Irish Potato Famine of the 1850s where millions of people starved because of the devastation wrought by this deadly disease..

tomato and potato late blight alert what every grower needs to know about tomato and potato late blight 13109 schavey rd., suite 7 dewitt, mi 48820 Late blight symptoms are similar on potato and tomato. With the exception of roots, all parts of the plants are susceptible, and leaves, stems, and fruit can be infected
Potato late blight is arguably one of the most infamous diseases in agriculture. Historically, it is best known as the cause of the Irish potato famine of the 1840s, which resulted in the death or emigration of over 2 million people from Ireland (Martin et al. 2013). Late blight is caused by the fungus-like comycete pathogen Phytophthora infestans. This potentially devastating disease can infect potato foliage and tubers at any stage of crop development. This potentially devastating disease can infect potato foliage and tubers at any stage of crop development.
Table 1. Tomato cultivars tested for late blight resistance against the US-22, US-23, and US-24 clonal lineages of Phytophthora infestans and their resistance/susceptibility response. Late blight, caused by the pathogen Phytophthora infestans , was a disease once considered sporadic, but is now an annual concern for tomato and potato growers in
This fact sheet explains the basics about late blight tomato disease and practical ways . to control it. Late blight (Phytophthora infestans) is one of the most serious fungal diseases that can affect tomatoes and potatoes. Late blight is spread from infected transplants, volunteer potato or tomato plants, How is it and certain weeds botanically related to tomatoes. Spores of this fungus can tomato and potato late blight alert what every grower needs to know about tomato and potato late blight 13109 schavey rd., suite 7 dewitt, mi 48820
Photo 1. Rapid destruction of tomato plants by late blight, Phytophthora infestans. Photo 2. Large irregular-shaped spots on the leaves, and rots on the fruit, of tomato caused Life cycle of Phytophthora infestans, causal agent of late blight of potato and tomato. The blight fungus parasitizes potato plants and closely related plants in South America. Farmers there grow an enormous number of potato cultivars that vary in their susceptibility to the parasite, so that even though some loss to the parasite occurs, devastating epidemics are avoided. The technology of
tomato and potato late blight alert what every grower needs to know about tomato and potato late blight 13109 schavey rd., suite 7 dewitt, mi 48820 Managing Late Blight in Tomato and Potato – An Essential Part of Gardening Meg McGrath, Department of Plant Pathology and Plant-Microbe Biology, Cornell University
Late blight is a community problem that threatens all potato and tomato growers. Everyone needs to do his or her part to prevent and control it. Phytophthora infestans symptoms (late blight) on potato stem in the field. Thorsten Kraska, University of Bonn, Germany Tuber blight on potato
Late Blight of Potato and Tomato May, 2018 Late blight is the most destructive disease of potato in British Columbia (B.C.). It is caused by Phytophthora infestans, an oomycete (fungal-like organism). Late blight is a destructive disease of tomatoes and potatoes that can kill plants, and make tomato fruits and potato tubers inedible. This disease also affects, although typically to a lesser extent, weeds such as nightshade. Historically, late blight was responsible, in part, for the Irish potato famine, which led to the death of at least one million Irish, and the emigration of another one
Late Blight (Phytophthora infestans) •Responsible for entire crop losses in the Solanaceae family such as tomato, potato, and eggplant in less than 5 days Managing Late Blight in Tomato and Potato – An Essential Part of Gardening Updated 3/31/2010 Prepared by Margaret Tuttle McGrath, Department of Plant Pathology and Plant-Microbe Biology, Cornell
Late Blight A Serious Disease of. Potatoes and Tomatoes Late Blight Symptoms. On potato tubers: Infected potatoes have shallow, brownish or purplish lesions on the surface of the tuber. Late blight affects foliage of both potato and tomato as well as potato tubers and tomato fruit. Late blight is a very difficult disease to manage organically. Organic farmers should employ all strategies available to reduce late blight risk in host crops.

Once late blight is present, only foliar fungicide applications can manage late blight in the field. (A current list of fungicides can be found in the NDSU “Fungicide Guide,” PP622). (A current list of fungicides can be found in the NDSU “Fungicide Guide,” PP622). Late blight is a community problem that threatens all potato and tomato growers. Everyone needs to do his or her part to prevent and control it.